Research field: Planning & Governance
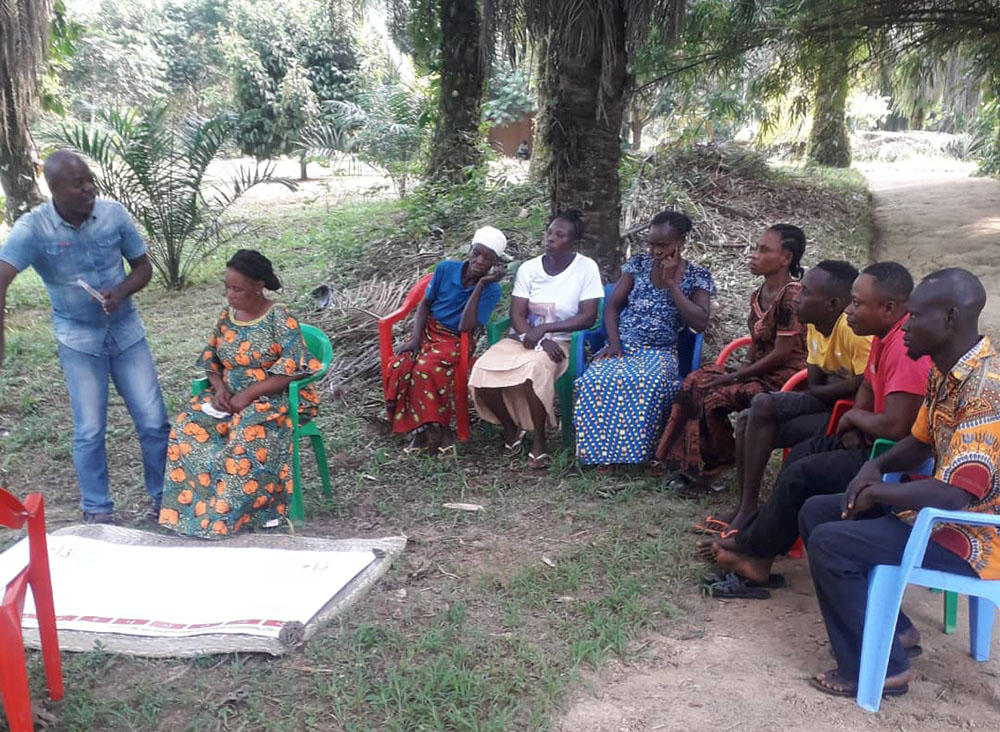

The DRC has over 100 million hectares of forest and has significant potential to benefit from these forests through REDD+ if they are managed effectively. The research shows that building the right capacity, consulting and accessing the needs of the community, and building long-term projects and partnerships are key success factors for improving forest governance.

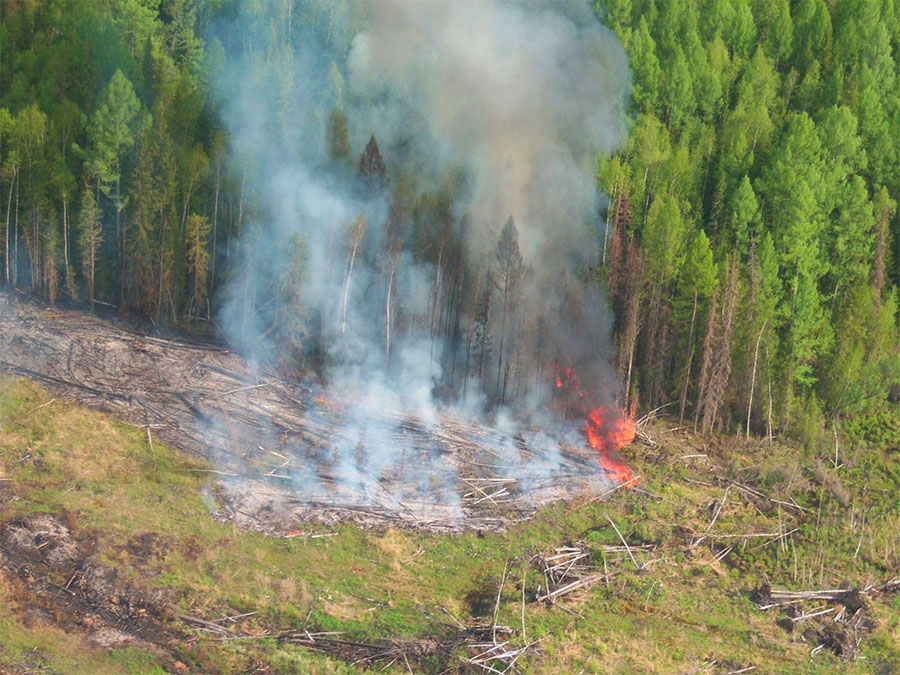
Payment for ecosystem service (PES) schemes are programmes that compensate forest communities for refraining from undertaking extractive uses, such as mining, intensive logging, and clearing. PES schemes can be important policy tools in meeting climate targets but effective deployment demands an understanding of local deforestation drivers and host communities’ preferences.

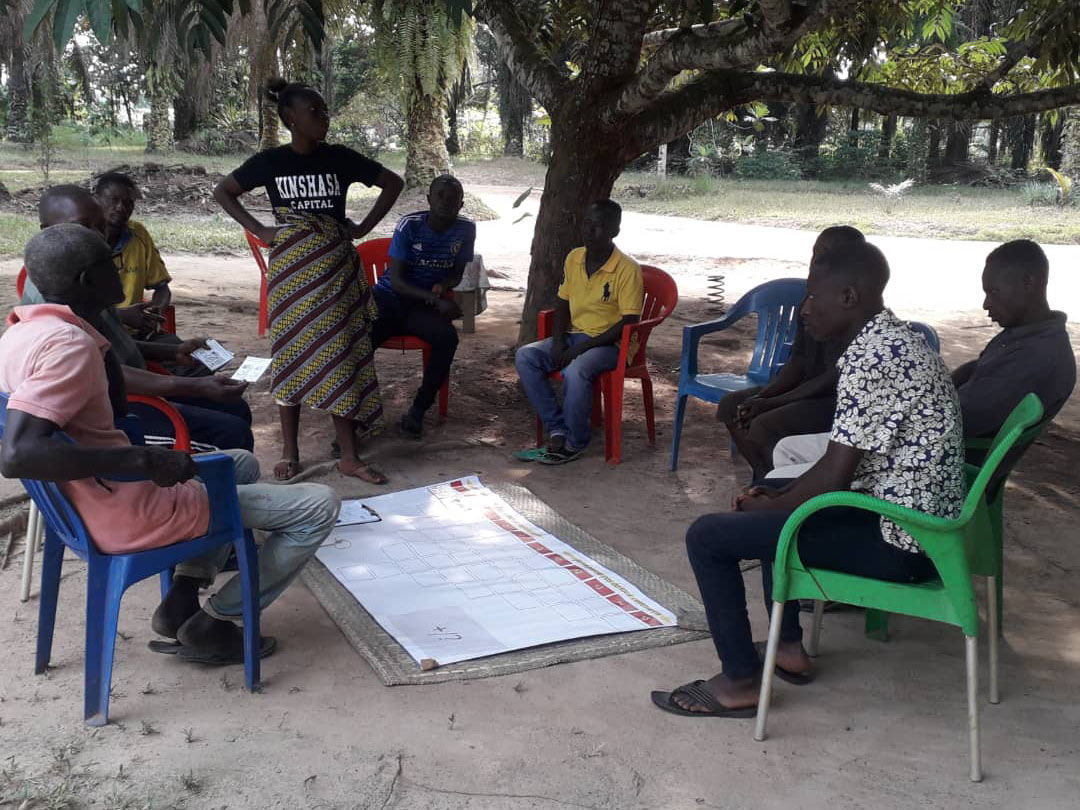
Effective planning is a key pillar of landscape management, but there are limited tools for evaluating planning, especially where planning is informal or nascent. This paper outlines a novel and robust principles, criteria and indicators framework for evaluating planning in contexts where there is limited formal planning.
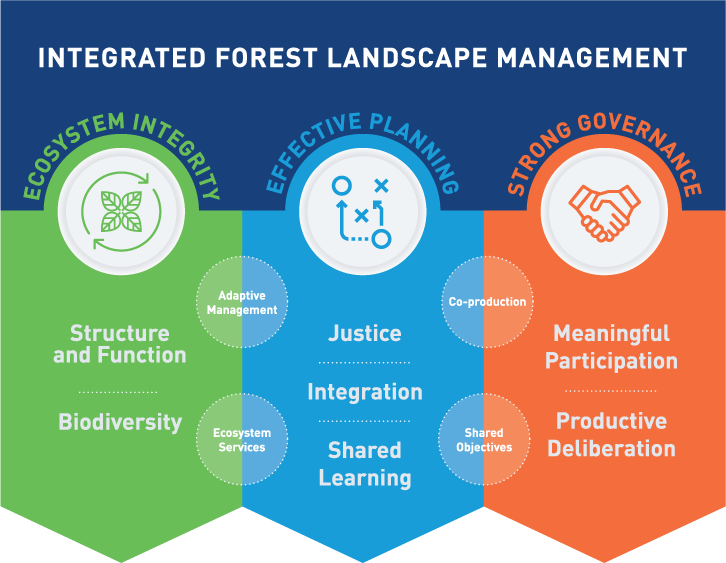
Integrated landscape approaches to forest management are more holistic than conventional sector-based approaches and provide a more promising approach to sustainable management. Integrity-based Forest Management (INFORM) provides a framework for developing and evaluating integrated landscape approaches built on ecosystem integrity, effective planning and strong governance.

Integrated landscape management of forest landscapes requires ecosystem integrity, effective planning and strong governance. Integrated landscape approaches to forest management are more holistic than conventional sector-based approaches and provide a more promising approach to sustainable management.






